The Intra2net system forwards DNS requests to the Internet. For details on how and where to set the currently active provider, see 10. Chapter, „Internet“.
It can also act as a DNS server for the local domain itself or delegate the task to another server.
If you do not have a full DNS server in your local network yet, use the Intra2net system as DNS server and configure it as described in this section. If you already use another DNS server (e.g. a Windows Domain Controller), proceed as described in Section 8.4.2, „Integrate another DNS server in the LAN“.
The individual host name and local domain can be set under Network > DNS > Settings. Specify that the local system is responsible for the local domain.
The Intra2net system is then the DNS server for the local domain. All host names entered under Network > Intranet > Clients can be resolved by DNS.
We strongly advise against using the official domain of a company (e.g."mycompany.com") in the local network. Since the Intra2net system is a DNS server for the local domain, it cannot answer requests from clients configured in the external DNS server of the web provider, such as "www".
Instead, use a locally valid domain, such as "mycompany.lan". Due to an Internet standard for broadcast DNS, we also advise against using ". local" for such domains, as some macOS or Linux versions do not support the name resolution when using ".local" in the local domain.
If using a different DNS server for the local domain (e.g. a Windows Domain Controller), enter the host name of the Intra2net system and the domain used in the local network under Network > DNS > Settings. Set the authority for the local domain to "". Enter the IP of the relevant DNS server and (if present) the alternative server in the "" and "" fields.
On these DNS servers, make sure to allocate an A-entry for the Intra2net system with its IP. For Windows Server, this is described in the following section.
If you use a Windows DNS server in the local network, it must be able to resolve the name and IP of the Intra2net system so that all computers in the local network can access the Intra2net system under its DNS name. Proceed as follows to create a DNS entry for the Intra2net system:
On the Windows server, open the DNS Manager from the menu "".
In the tree on the left, open the forward lookup zones of your server.
Right-click on the local domain you are using and select "" from the context menu.
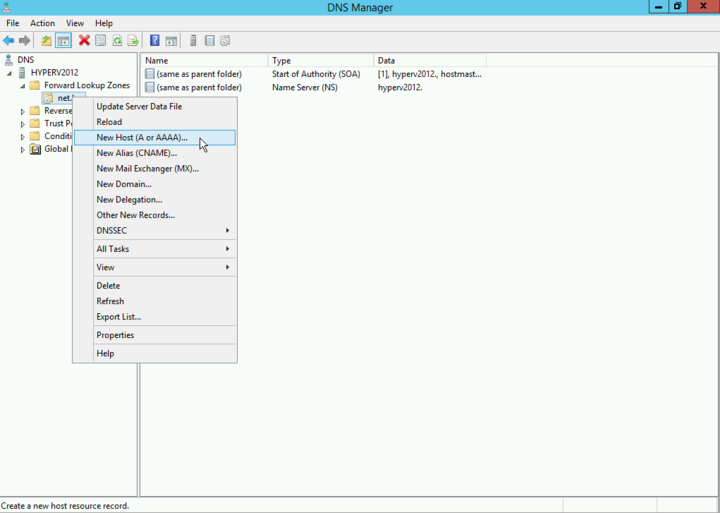
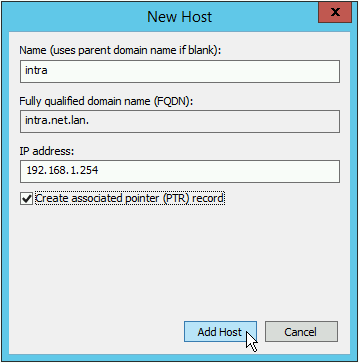
Enter the name and IP of the Intra2net system. Create an associated pointer (PTR) record.
The Intra2net system can forward requests for other non-public domains to dedicated servers. This is useful, for example, if different locations are connected via VPN and names in the local domains of the other locations are to be resolvable.
Enter the domains and IPs of the corresponding DNS servers under Network > DNS > Forwarding.
During a "DNS rebinding" attack, an external DNS server returns an IP from the local network. This may allow an external attacker to force a web browser to establish a remote connection to the local network. Details about this type of attack can be found on Wikipedia.
The Intra2net system can effectively prevent these attacks by blocking responses with local IPs from external DNS servers. To avoid malfunctions, only real external DNS servers should be entered under Network > Provider > Profiles : Settings.
All DNS servers that are responsible for local or locally routed domains must be configured for DNS forwarding under the relevant domains. The servers stored there may then respond with local IPs.
Windows DNS servers do not have their own protection against DNS rebind attacks. If you are using a Windows DNS server on the local network and have configured it as described in Section 8.4.2, „Integrate another DNS server in the LAN“, proceed as follows to protect it from DNS rebind:
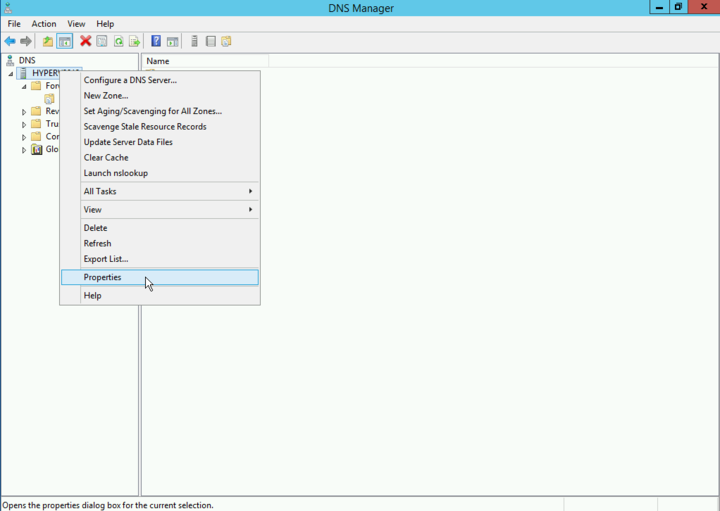
On the Windows server, open the DNS Manager from the menu "".
In the tree on the left, right-click on the DNS server name and open the "" context menu.
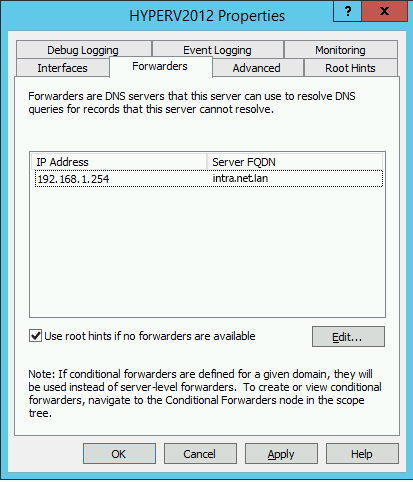
Switch to the "" tab and click "".
Enter the IP of the Intra2net system and remove all other entries (e.g. gateway or DNS server of the Internet provider).
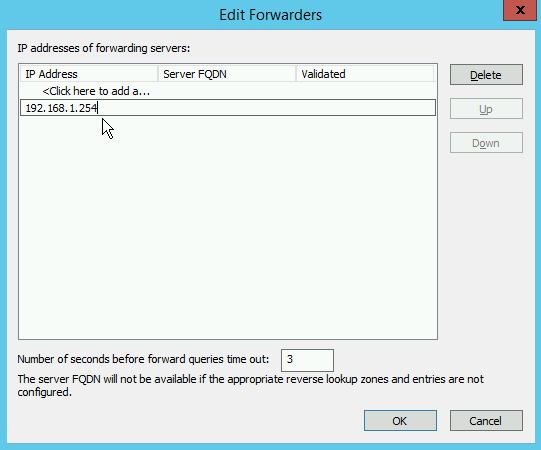
Now only the Intra2net system is displayed in the forwarders overview. All DNS requests to the Internet now run through the Intra2net system and are protected against DNS rebind.